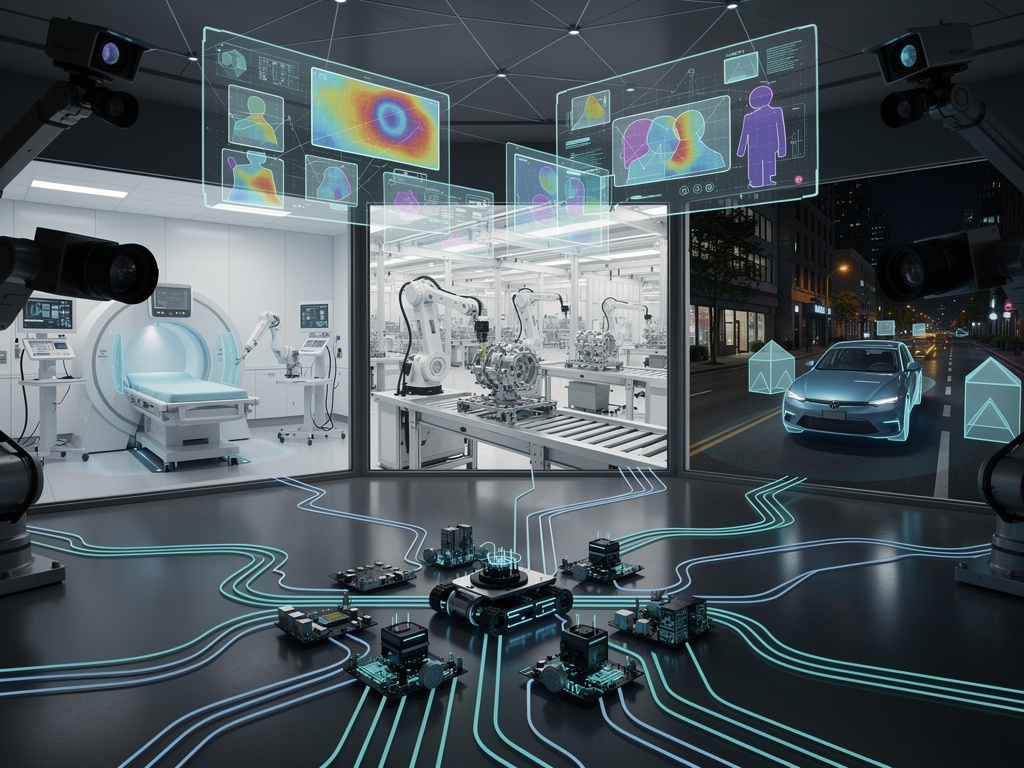
In the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence, machines are no longer mere tools but entities capable of perceiving the world with astonishing acuity. Recent advances have enabled them to see, learn from visual data, and make decisions that rival human intuition. This shift is transforming sectors from manufacturing to healthcare, where AI systems analyze images, predict outcomes and act autonomously. Taken from a video report by MSNwhich explores these capabilities through expert insights and real-world examples, we examine how these technologies are reshaping our interaction with intelligent systems.
The heart of these advances lies in machine vision, a field that allows computers to interpret visual information from the world. Algorithms now process images and videos precisely, identifying objects, tracking movements and even understanding contexts. For example, in industrial environments, vision systems inspect products for defects at speeds unattainable by humans. It’s not just about speed; it’s about precision and scalability, enabling continuous operation without fatigue.
Advances in deep learning have enhanced these capabilities. Neural networks, trained on large datasets, can now recognize patterns that were once elusive. Integrating AI with vision technology means machines don’t just see: they understand. This understanding extends to decision-making, where AI evaluates options based on visual inputs and historical data, choosing the optimal path forward.
Pushing the limits of visual perception
A crucial development is the rise of models like NeRF and CLIP, which are revolutionizing the way machines process visual data. As detailed in a blog post from Crazy developersthese algorithms are expected to generate a market worth $29.27 billion by 2025, impacting sectors like autonomous vehicles and medical imaging. NeRFs, for example, create 3D reconstructions from 2D images, enabling virtual reality applications that appear realistic.
At the same time, deep learning models improve decision-making processes. AI systems now incorporate reinforcement learning, where they learn through trial and error, refining their choices over time. This is evident in robotics, where machines navigate complex environments by visually assessing obstacles and planning routes. Articles on
The ethical implications are profound. As AI makes decisions based on visual learning, questions arise regarding biases in the training data. If data sets tilt in favor of certain demographics, decisions could perpetuate inequalities. Industry experts emphasize the need for diverse data sources to ensure equitable outcomes, a point echoed in recent discussions on governance challenges.
Integration across all sectors
Healthcare is the biggest beneficiary of these technologies. Machine vision helps diagnose diseases through image analysis, such as detecting tumors during scans with greater accuracy than traditional methods. An editorial from the Frontiers journal of Borders notes how deep learning models are generating practical applications, from early detection to personalized treatment plans. This not only speeds up diagnostics, but also reduces human errors.
In the manufacturing sector, under the banner of Industry 4.0, vision systems integrated with AI enable predictive maintenance. Cameras monitor equipment and learn to spot wear and tear before failures occur, minimizing downtime. According to an article from ScienceDirectthe high volume of data from visual equipment is the cornerstone of this digital shift, fostering a culture of efficiency and innovation.
Decision AI extends to strategic levels. Businesses use these systems to make data-driven choices, analyzing visual trends in market data or consumer behavior. An article from London Business News Londonlovesbusiness.com explains how AI improves strategic thinking by processing large amounts of information, transforming raw data into actionable insights.
Emerging trends and challenges
Looking ahead, 2025 promises even more sophisticated integrations. Google’s search advancements, as described in their blog at blog.googleinclude new AI models that advance robotics and scientific discovery. These models improve visual understanding, allowing machines to interpret complex scenes like crowded urban environments or complex biological structures.
On X, enthusiasts share their enthusiasm for agentic AI, where systems act autonomously. One paper describes Qwen2.5-VL, a Chinese vision language model that excels in visual understanding and agent capabilities, interacting with tools such as computers and phones. This reflects a broader movement toward AI that not only sees and learns, but also reasons and performs tasks independently.
However, challenges persist. Data privacy issues are of great importance, especially in vision-based systems that capture personal images. Ensuring secure processing of this data is crucial, as is meeting the energy requirements associated with training large models. Industry reports emphasize sustainable practices, such as optimizing algorithms for lower computing needs.
Concrete applications and future perspectives
Autonomous vehicles illustrate the pinnacle of these technologies. Edge AI inference enables real-time decision-making based on sensor data, avoiding reliance on cloud servers. An article from
In agriculture, drones equipped with machine vision monitor crops, learning to identify diseases or nutritional deficiencies. This data informs decisions about irrigation or pesticide use, increasing yields while minimizing environmental impact. The Ultralytics blog on Ultralytics highlights applications such as object detection and pose estimation, transforming agriculture into a precision science.
Education also benefits, with AI tutors using visual recognition to gauge student engagement and adapt lessons accordingly. By learning facial expressions and body language, these systems make informed decisions about instructional strategies, personalizing education at scale.
Ethical frameworks and governance
As these technologies proliferate, it becomes imperative to establish strong ethical frameworks. An article from Bioengineer.org on Bioengineer.org discusses the challenges of AI for liver cancer, highlighting the need for governance in healthcare AI to ensure equitable access and accurate diagnoses.
International collaboration is essential. Governments and organizations are developing policies to regulate AI decision-making, particularly in critical areas like finance and security. Recent news from TechGig on Technology concert provides a roadmap for professionals, emphasizing skills in deep learning and ethical AI practices.
Additionally, merging AI with emerging technologies like 5G and IoT amplifies capabilities. An Automate.org blog from Automate.org details how these integrations improve industrial automation, enabling faster data transmission and real-time decision-making.
Innovations in learning mechanisms
Advances in continuous learning ensure that AI systems adapt over time without forgetting prior knowledge. X articles list key concepts such as reinforcement learning and neuro-symbolic AI, which combine neural networks with symbolic reasoning for more robust decision-making.
In creative fields, generative AI produces visuals based on learned patterns, moving from novelty to practical tools. An article on X maps the 2025 ecosystem, including frameworks like LangGraph for multi-agent systems, signaling maturity in AI orchestration.
These innovations are not without risks. Over-reliance on AI for decisions could diminish human oversight, leading to unforeseen errors. Balancing automation and human judgment remains a crucial point of discussion among experts.
Growing for global impact
The 3D mapping and modeling market is booming, driven by smart city initiatives. Newstrail reports at News feed project it to reach $23.15 billion by 2032, powered by AI-enhanced geospatial technologies that aid urban planning and disaster response.
In defense and security, machine vision detects threats through pattern recognition, leveraging vast surveillance data to make preventative decisions. This app requires strict ethical standards to avoid misuse.
Globally, AI’s role in climate monitoring uses satellite imagery to track changes and inform policy decisions. By learning from visual trends, the systems predict environmental changes, thereby contributing to mitigation strategies.
The road ahead in the evolution of AI
Faced with these developments, education and skills development are essential. Case Western Reserve University’s online program, as mentioned in Cas.eduprepares engineers for the complexities of AI, focusing on algorithms and systems control.
Marine agronomy guide on Marineagronomy.org explores trends like Missax New, highlighting innovations happening in digital fields.
Finally, the synergy between vision, learning and decision-making positions AI as the cornerstone of future progress. Industry players expect even deeper integrations, in which machines not only see and decide, but anticipate needs, fostering a more intuitive technology ecosystem. This development, although promising, calls for vigilant management to exploit its full potential responsibly.