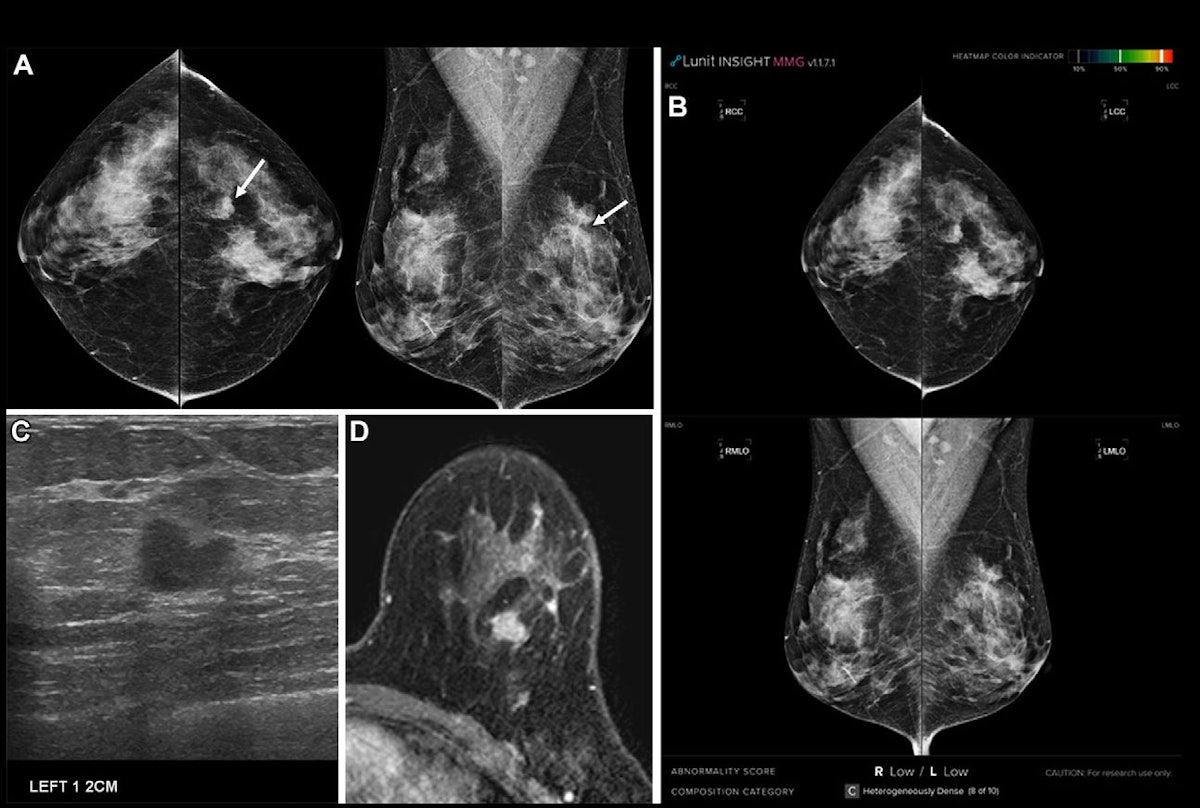
According to a study published on June 24 in radiology.
These characteristics include luminal cancers, dense breast tissues, the locations of non -breast zones, architectural distortions and amorphous calcifications, wrote a team led by OK Hee Woo, MD, from Korea University Hospital to Seoul.
“Although AI is useful to detect invasive cancers at an advanced stage, it is inadequate to identify cancers with some of the characteristics revealed in this study,” noted the group. “Understanding the characteristics of invasive cancers Missés on mammograms can help readers use AI appropriately in clinical practice, thus contributing to its additional optimization.”
AI has become considered a promising tool to help read mammograms, but he can always miss breast cancers, Woo and his colleagues have written. Few studies have assessed the rate of fake negatives of the mammography of IA-reading in invasive cancers, and the “clinicopathological and radiological characteristics of IA invasive cancers and the reasons for missing cancers remain under-explorated”.
The group studied the rate of false negatives of AI mammograms by molecular subtype (positive hormonal receiver [luminal] vs receiver of the human epidermal growth factor 2 [HER2]-Eriche in relation to triple negative) and followed the characteristics and reasons for these missed cancers. The study of the team included 1,082 women diagnosed with 1,097 cancers between January 2014 and December 2020.
Commercial AI software has been used to read mammograms (Lunit Insight MMG). The cancers missed by AI have been defined as “those for which AI has not identified a specific location corresponding to the reference standard”. Three radiologists, blind, whether breast cancer had been missed by i-Mammography, classified cancers as “exploitable” or “under the threshold”; Readers are aware of the failed Cancers on AI have determined the reasons for the reasons for failures in a new review.
The AI missed 154 of the 1,097 cancers (14%). These missed cancers had the following characteristics:
- They were found in younger women.
- The size of the tumor was less than or equal to 2 cm.
- They had a lower histological quality and fewer lymph node metastases.
- More of them have been classified as Bi-Rads 4.
- Cancers had a lower expression of Ki-67 and fewer of non-breast zone sites.
Among the cancers missed by AI, 61.7% were achievable, revealed the researchers. Other reasons for missing included dense breast tissue (n = 56), the locations of non -breast zones (n = 22), architectural distortions (n = 12) and amorphous microcalcifications (n = 5).
Regarding the rate of false negatives, the team also reported the following:
|
False negative rate of AI mammography by breast cancer subtype * |
|
|
Breast cancer type |
False positive rate |
| HER2 Enriched |
9% |
| Luminal |
17.2% |
| Triple negative |
14.5% |
| * All statistically significant results | |
In an accompaniment editorial, Lisa Mullen, MD, of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, urged radiologists using AI with mammography to “pay particular attention to dense breasts and non -mammative areas, as well as in carefully research distortion, microcalcifications and small lesions.”
“When using AI, it is essential that radiologists understand what could be potentially missed by the software so that [they] Can use information to reduce the chances of missed cancer, “she concluded.
The full study can be found here.