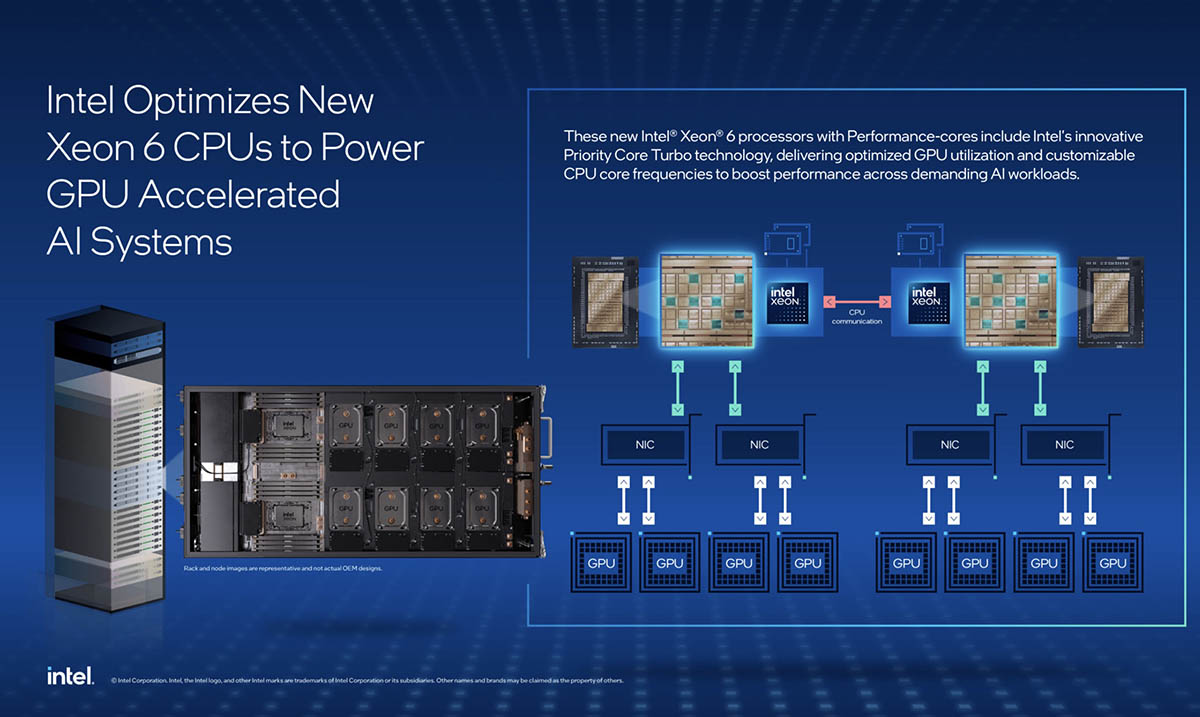
Today, we have one that we found quite surprising. Intels now its SST features as a functionality for NVIDIA GPU servers. This is the one we have done much more in depth in our Intel Xeon 6 cores of high priority and low priority explained. However, it is at least interesting.
Intel Xeon 6 priority cores as a great functionality Nvidia gpu ai server
In the next NVIDIA DGX B300, NVIDIA uses Intel Xeon 6776p. It is a cache piece of 64 cores, 350W, 336 MB L3. This is a big problem because winning a reference Nvidia socket generally means that a large number of customer systems on the HGX side will use the same processors.
There was a little marketing that we should call Liberation of Intel.
By looking more broadly, the Intel Xeon 6 processors with P-Cores offer advanced features for any AI system, in particular:
- Number of high nucleus and exceptional unique thread performance: With up to 128 Cores P by CPU, these processors guarantee a balanced workload distribution for intensive AI tasks.
- 30% faster memory speeds1:: Compared to competition, Intel Xeon 6 offers superior memory performance to high -capacity configurations and supports the bandwidth of attack memory with Mrdimms and Calculates Express Link…
1 Configuration of 2DPC memory configuration, 2DPC on an Intel Xeon 6700p processor = 5200 mt / s RDDIMM SPEED; 2DPC on the latest AMD Epyc processor = 4,000 mt / s Radimm Speed (Source: Intel)
The 128 p by CPU are in the Intel Xeon 6900p series, which is a different socket from the XEON 6700P series which is used in the NVIDIA DGX B300.
On “memory speeds”, this is very reflected because Intel compares 2DPC XEON 6700P and the 2DPC AMD EPYC 9005, only looking at speed. One of the reasons why the AMD EPYC 9005 drops memory speeds in 2DPC mode is that it has 50% more memory channels. These additional channels create longer traces and there is therefore a drop in speed.
If you executed a 2DPC at 12 channels on the EPYC 9005 AMD compared to the Intel Xeon 6700p than Intel compare, you find yourself both with more memory capacity and more memory bandwidth because you have 24 dimms per socket and 12 memory channels at 4000 mt / s against 16 DIMM by Sockts and 8 channels at 5200MT / S. What is also remarkable is that if you only need the capacity of 12 DIMMS, you can run the Xeon 6900p with MCR DIMMS / MRDIMMS or EPYC 9005 at DDR5-6400 to obtain a mixture of capacity and performance while adjusting side by side in a 19 ″ rack form factor.
On the subject of Mrdimms because they are mentioned, if you use them, you will use CPUs in 1DPC mode, not 2DPC mode. This gives you speeds of 8000 Mt / s on the XEON 6700P with 8 channels and 8 DIMM. The AMD comparison is 6,400 mt / s with 12 channels and 12 DIMMS giving you more capacity and bandwidth.
Last words
Let’s go to what is really going on here. We often cannot show the NVIDIA GPU GPU servers fed by AMD, because Nvidia does not want her chips to be marketed alongside her main competitor GPU. With Intel, Nvidia does not see an important competitor because Broadcom and AMD are much greater threats to the AI market. Therefore, the use of Xeon with Nvidia GPUs is preferred. Intel Xeon is in many ways the beneficiary of Rialto Bridge and Falcon Shores who does not arrive at the market.
Despite the fact that Intel plays it quite loose with marketing here, being in the reference design Nvidia DGX is a big problem. Many reference conceptions use the same processors as NVIDIA used in the DGX. In the future, Nvidia has shown partners that he plans to standardize not only the HGX 8-GPU plinth, but also the entire design of the motherboard, while it continues during his MGX trip. This will excite the importance of gaining NVIDIA reference take.