Editor’s note: This article is part of In the Omniversea series focused on how developers, 3D practitioners and businesses can transform their workflows using the latest advancements in OpenUSD And NVIDIA Omniverse.
Open source has become essential to drive innovation in robotics and autonomy. By providing access to critical infrastructure – from simulation frameworks to AI models – NVIDIA enables collaborative development that accelerates the transition to safer, more capable autonomous systems.
At CES earlier this month, NVIDIA showed off a new open source software suite Physical AI models and frameworks to accelerate the development of humanoids, autonomous vehicles and other physical embodiments of AI. These tools span the entire robotics development lifecycle – from high-fidelity global simulation and synthetic data generation to cloud-native orchestration and edge deployment – providing developers with a modular toolkit for building autonomous systems capable of reasoning, learning and acting in the real world.
OpenUSD provides the common framework that standardizes how 3D data is shared between these physics AI tools, allowing developers to create digital twins and reuse them seamlessly, from simulation to deployment. NVIDIA Omniverse The libraries, built on OpenUSD, serve as the ground truth simulation source that powers the entire stack.
From laboratories to the exhibition hall
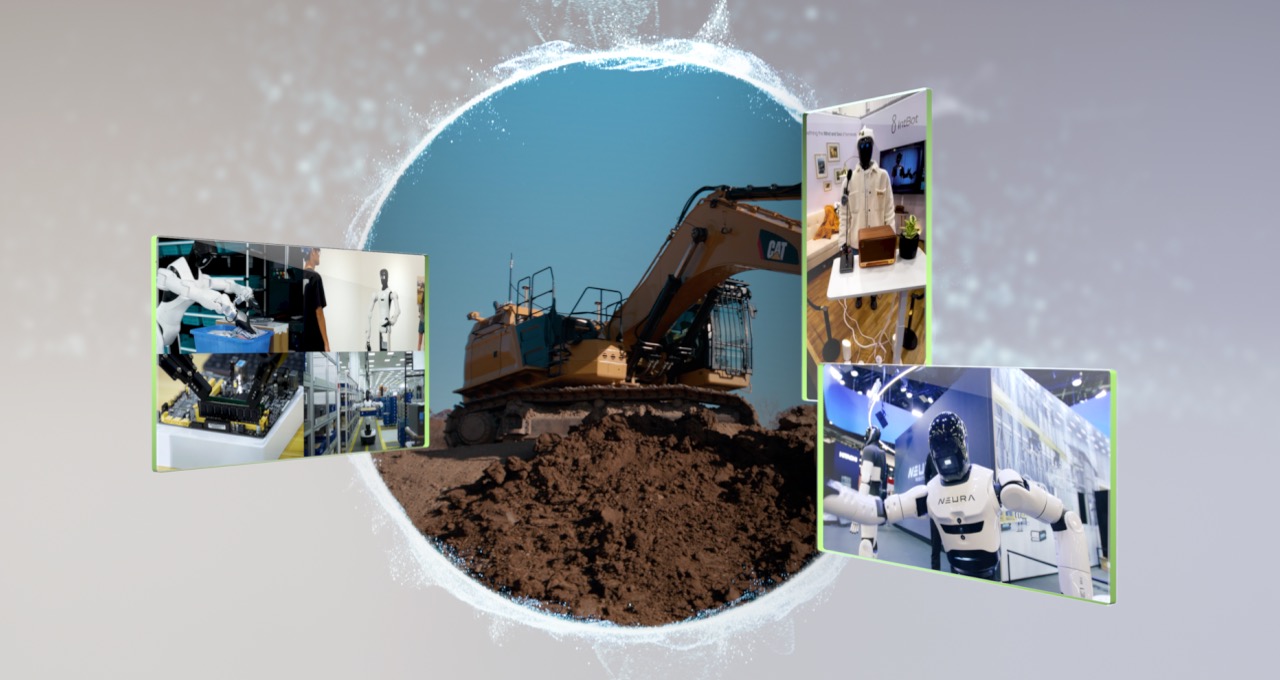
At CES 2026, developers took the NVIDIA physical AI stack out of the lab and onto the show floor, launching machines ranging from heavy equipment and factory assistants to social and service robots.
The stack uses NVIDIA Cosmos global models; NVIDIA Isaac technologies, including the new Isaac Lab-Aréna open source framework for policy evaluation; THE NVIDIA Alpamayo open portfolio of AI models, simulation frameworks and physics AI datasets for autonomous vehicles; and the NVIDIA OSMO framework for orchestrating training in IT environments.
CaterpillarThe Cat AI assistantpowered by NVIDIA Nemotron open models for agentic AI and running on the NVIDIA Jetson Thor Edge AI module, bring natural language interaction directly into the cabin of heavy vehicles. Operators can ask “Hey Cat” questions and get step-by-step guidance, as well as adjust security settings by voice.
Behind the scenes, Caterpillar uses Omniverse libraries to create factory and jobsite digital twins that can help simulate configurations, traffic patterns and multi-machine workflows. This information is fed back into equipment and fleets before changes are deployed on job sites, making AI-assisted operations safer and more efficient.
LEM Surgical presented its Dynamis robotic surgical system, approved by the FDA and used in routine clinical settings for spinal procedures. The next generation system uses NVIDIA Jetson AGX Thor for computing, NVIDIA Holoscan for real-time sensor processing and NVIDIA Isaac for Healthcare to train its autonomous arms.
LEM Surgical also uses NVIDIA Cosmos Transfer — an open, fully customizable global model that enables physically-based synthetic data generation — to generate synthetic training data and the NVIDIA Isaac Sim framework for digital twin simulation. Designed as a two-armed humanoid surgical robot for hard tissue surgery, the Dynamis system mimics the dexterity of the human surgeon and enables complex spinal procedures with increased precision, alleviating the intense physical demands of surgeons and surgical assistants.
NEURA Robotics builds cognitive robots on a full NVIDIA stack, using Isaac Sim And Isaac Laboratory to train its 4NE1 and MiPA humanoid service robots as OpenUSD-based digital twins before their deployment in home and workplace environments. The company used NVIDIA Isaac GR00T-Mimic to post-train the Isaac Foundation GR00T model for its platforms.
Additionally, NEURA Robotics is collaborating with SAP and NVIDIA to integrate SAP’s Joule agents with its robots, using the NVIDIA Omniverse Mega Plan simulate and refine robot behavior in complex and realistic operational scenarios before those agents and behaviors are deployed into the company’s Neuraverse ecosystem, as well as real-world fleets.
AgiBot uses NVIDIA Cosmos Predict 2 as the world modeling backbone for its Genie Envisioner (GE-Sim) platform, enabling the platform to generate action-conditioned videos based on strong visual and physical backgrounds. Combining this data with Isaac Sim and Isaac Lab, along with post-training on AgiBot’s own data, allows policies developed in Genie Envisioner to be more reliably transferred to Genie2 humanoids and compact tabletop robots powered by Jetson Thor.
Intbot uses the NVIDIA Cosmos Reason 2 open model to give its social robots a “sixth sense” for the real world – using the model’s reasoning capabilities to identify simple social cues and safety context that go beyond simple scripted tasks. In his Recipe from Cosmos CookbookIntbot demonstrates how reasoning from vision language models can help robots decide when to speak and how to interact more naturally with humans.
How robotics developers are using new toolkits and frameworks
NVIDIA recently introduced Agile, an Isaac Lab-based engine for humanoid locomotive manipulation that brings together a complete, simulation-to-real-world verified workflow for robust training. reinforcement learning policies on platforms like Unitree G1 and LimX Dynamics TRON.
Robotics developers can use Agile’s built-in task configurations, Markov decision process mathematical models for decision making, training utilities, and deterministic evaluation tools to adjust policies. Developers can then test these policies in Isaac Lab and transfer locomotion and whole-body behaviors to real-world robots more reliably and efficiently.
Hugging Face and NVIDIA are bringing their robotics communities together by integrating NVIDIA Isaac GR00T N models and simulation frameworks into the LeRobot ecosystem. Developers can now access the Isaac GR00T N1.6 and Isaac Lab‑Arena models directly in LeRobot to streamline training and policy evaluation.
Additionally, Hugging Face’s open source Reachy 2 humanoid is now fully interoperable with NVIDIA Jetson Thor, enabling direct deployment of advanced Vision Action Language (VLA) models for robust real-world performance.
ROBOTICSa leading developer of intelligent servos, industrial actuators, manipulators, open source humanoid platforms and educational robotics kits, has built an open source simulation-to-reality pipeline using NVIDIA Isaac technologies. The workflow begins with generating high-fidelity data in Isaac Sim, extends the training sets using GR00T-Mimic for augmentation, and then refines a VLA-based Isaac GR00T N model that deploys directly to hardware, accelerating the transition from simulation to robust real-world tasks.
Be connected
Learn more about OpenUSD and robotics development by exploring these resources:
- Read this technical blog to learn how to develop general humanoid capabilities with NVIDIA Isaac and GR00T N1.6.
- Read this technical blog to learn how to evaluate general robot policies in simulation using NVIDIA Isaac Lab – Arena.
- Learn how to post train Isaac GR00T with this two-part video tutorial.
- Watch Jensen Huang, founder and CEO of NVIDIA CES Special Presentation.
- Improve skills for robotics development at your own pace robotics learning path.
- Participate in the Cosmos cuisinea hands-on physics AI challenge in which developers use Cosmos Reason to power robotics, autonomous systems, and vision AI workflows.