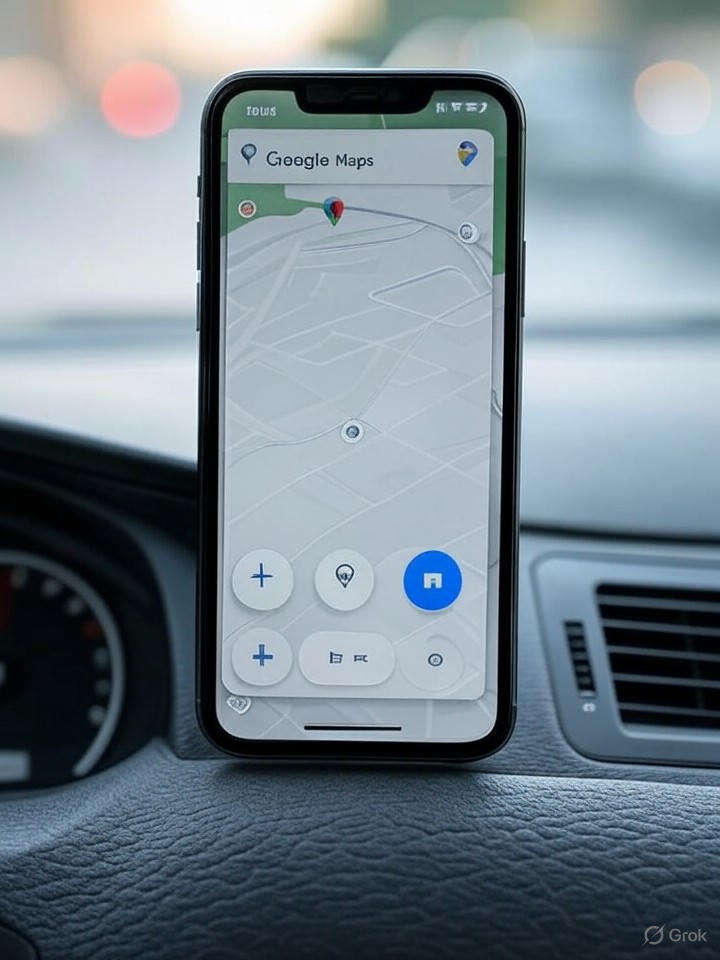
In the ever-changing world of mobile navigation, Google has introduced subtle but impactful changes to its Maps app, particularly improving the user experience for drivers using Android Auto. According to a recent report from TechRadarThe latest change involves a redesigned interface that makes key controls more accessible on the road, addressing long-standing complaints about usability during active navigation. This update allows drivers to quickly adjust settings without taking too much of their attention away from driving, a move that underscores Google’s commitment to the safety and efficiency of automotive integrations.
Beyond the immediate usability improvements, the update hints at broader implications for how navigation apps integrate with vehicle systems. Industry analysts note that as Android Auto gains traction on more car models, such improvements could set new standards for competitors like Apple CarPlay, potentially influencing automotive software partnerships. The change, which repositions essential buttons for easier access, comes amid increasing functionality in connected cars, where smooth app performance can make or break user loyalty.
Improve battery efficiency in browsing
Looking ahead, Google Maps is set to roll out a feature that could revolutionize battery management for mobile users. As detailed in the same TechRadar article, an upcoming power-saving mode could switch the app to a monochrome interface while browsing, reducing power consumption by minimizing the colorful rendering that drains device batteries. This development, spotted in beta versions, addresses a common problem for users on long trips where charging the phone is not always possible.
For industry insiders, this battery-saving innovation represents a strategic pivot toward sustainability in app design. Reports of T3 suggest that this mode could significantly extend navigation time, even on low battery, by simplifying visuals without compromising basic features such as route guidance. Such features align with growing consumer demands for eco-friendly technology, potentially giving Google an advantage in markets where battery life is a key differentiator.
Implications for automotive technology integration
The Android Auto interface setting is not isolated; It’s part of a pattern of iterative improvements that Google has been pushing. For example, previous updates reported by Tom’s guide enabled the simultaneous use of maps on the phone and car screen, improving multitasking for passengers or when changing devices. This latest change builds on that foundation, making controls more intuitive and reducing the cognitive load on drivers, which could reduce the risk of accidents associated with in-car distractions.
Additionally, as electric vehicles proliferate, efficient battery use in applications becomes paramount. Previews of Android Center highlight how monochrome mode could be particularly beneficial for electric vehicle owners heading to charging stations, preserving phone power for critical moments. This positions Google Maps as a more robust tool in the connected mobility ecosystem, where app reliability has a direct impact on user trust and adoption rates.
Future directions and competitive pressures
Google’s continued improvements reflect a data-driven approach to user feedback, with features such as visual directions, previously covered in a TechRadar updated, already simplifying navigation on the go. The potential battery saving mode, if fully implemented, could expand to other Google services, promoting a more integrated Android experience. However, competitors like Waze and Apple Maps aren’t standing still, with their own updates focused on real-time traffic and augmented reality overlays, forcing Google to continually innovate.
For technology managers and developers, these changes highlight the importance of cross-platform optimization. As noted on the cover of PhoneArenaEven minor design changes can improve safety and driver satisfaction, and potentially influence regulatory standards for in-vehicle applications. Ultimately, Google’s strategy not only refines the user experience but also strengthens its dominance in navigation, paving the way for more advanced features such as AI-based route predictions in the coming years.